class Person
{
public:
typedef double Inches;
typedef double Pounds;
public:
Person();
void SetWeight(Pounds weight);
void getHeight(Inches height);
};
void f (const Person& person){
Person::Inches height = person.getHeight();
person.SetWeight(height); // 这里不会因为 height 的类型不是 Pounds 而报错 }
声明复杂的类型
typedef int (Person::*PCPMFDI)(double) const; // 声明一个指针类型, // 指向 const person 成员函数 // 参数类型为 double // 返回类型为 int
开发工作完成后,设置preprocess 预处理 NDEBUG,可以将所有的 assert 语句都去掉。 注意:assert 中应该只判断不要操作对象。
class String
{
public:
enum {DEFAULT_SIZE = 8};
char *d_array_p;
int d_size;
int d_length;
public:
String();
};
String::String()
{
assert(d_array_p = new char[d_size]); // 错误: assert 中应该只判断
// 不要操作对象,否则会使 prod
// 的版本和 debug 的版本行为不
// 同。因为 prod 版 用 NDEBUG
// 去掉了所有 assert.
// 可以这样写
d_array_p = new char[d_size];
assert(d_array_p);
}
其他知识点: 类 member variable 代表对象的状态,改变他们,就是改变对象的状态
按照功能排列 methods, 如示例代码, 每组将methods 按字母顺序排列
class Car
{
// 按照功能排列 methods
public:
// CREATORS 生成和取消对象
Car(int cost = 0);
Car(const Car& car );
~Car();
// MANIPULATION 就是 non const method members
// 将methods 按字母顺序排列
Car& operator=(const Car& car);
void addFuel(double numberOfGallons);
void drive(double deltaGasPedal);
void turn(double angleInDegree);
// ACCESSORS 都是 const method members
double getFuel() const;
double getRPMs() const;
double getSpeed() const;
}; 不要将 getXXX() setXXX() 排在一起。这样容易暴露 XXX(variable member)的行为。
看下面的例子:
class IntSet
{
public:
// DATA
intSetLink *d_root_p; // root of a linked list of integers
// FRIENDS
friend intSetIter;
private:
// NOT IMPLEMENTED
IntSet(const IntSet&);
// 禁止 code client 通过拷贝构造 IntSet
IntSet& operator= (const IntSet&);
// 禁止将一个 IntSet 赋值给另一个 IntSet
public:
// 允许创建,销毁和添加 int 到 IntSet,
// 允许检查关系
// CREATORS
IntSet();
// Create an empty set of integers
~IntSet();
// Destroy this set
// MANIPULATORS
void add(int i);
// Add an integer to this set. If the given integer is
// already present, this operation has no effect.
// ACCESSORS
int isMember(int i) const;
// Return 1 if integer i is a member of the set
// and 0 otherwise
}; ## 逻辑设计表示法
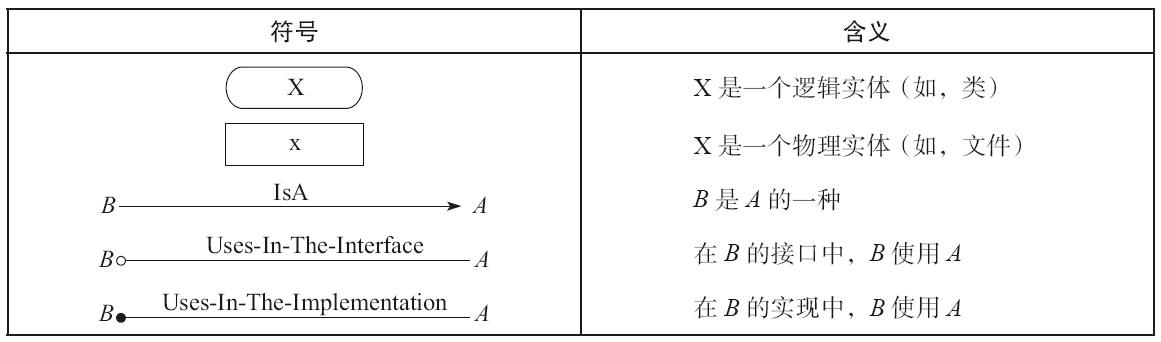
常用的逻辑设计符号,用来表示逻辑实体之间的关系。

圆角矩形表示逻辑实体: class, struct, union
长方形表示物理实体: object
常用的三种逻辑符号:
public 继承, 箭头表示依赖的方向, D 指向 B.
Uses-in-interface 的意思是说,一个函数的 signature 或者 返回类型中使用了某个 class/type。或者在类的接口 public member methods 使用了某个 class/type;
Uses in the implementation 的意思是,一个函数的定义中涉及了一个类型。分三种情况:
下面的代码中,operator == 对 IntSet 有 use-in-interface 的依赖关系,对 IntSet 有 use-in-implementation 的依赖
int operator ==(const IntSet& left, const IntSet& right){
IntSetIter lit(left);
IntSetIter rit(right);
for(; lit && rit; ++lit, ++rit){
if(lit() != rit())
return 0;
}
// At least one of lit and rit now evaluates to 0
return lit == rit;
}
Uses 类的成员函数中命名了一个类型
class Crook {
private:
void bribe();
...
};
class Judge; void Crook::bribe() { Judge *bad = 0; // Crook use Judge }
HasA 和 HoldsA
HasA: 类 X 嵌入一个 private member, 其类型为 T
HoldsA: 类 X 包含一个 member,其类型是从 T 派生而来的,比如 T* 或 T&.
下面的例子中,BattleShip HasA Tower, Holds 2 Cannons:
class Tower {};
class Cannon;
class BattleShip
{
Tower d_controlTower;
Cannon *d_replaceableForwardBattery_p;
Cannon& d_fixedAftBattery;
public:
BattleShip();
};
// BattleShip HasA Tower, Holds 2 Cannons:
WasA 特指私有继承
下面的例子中,ArizonMemorial wasA Battleship, hasA Shop, holdsA Exihibit
class Battleship{};
class Shop {};
class Exhibit; // declaration only
class ArizonaMemorial : private Battleship
{
Shop d_giftShop;
Exhibit *d_current_p;
Exhibit& d_default;
//...
};
layering 的定义:如果一个类A在其 implementation 中使用了另一个类型B (hasA, HoldsA,或者 A 由 B 组成),则类A基于类型B,类型B所在的 layer 位于类 A 所在 layer 之下. 我们通常不能通过高层的接口来访问底层的对象。也就是 B 不应该出现在 A 的接口中。B 是 A 内部的实现细节。
例子, Person hasA heart, liver, brain, 但是 Person 在工作的时候,不需要将 heart, liver, brain 暴露在 interface 上。
用不到的功能不实现。